Lecture 21: OS Security 1
Exam
Security and its management in the OS
Important questions:
- Can you define safety and security?
- What is the task of OS security?
- Can you give examples for malware?
- What is the difference to social engineering?
- Which types of malware exist, can you define them?
- What is permission management and what are the related requirements?
- What is the principle of least privilege?
- Define the access matrix and describe the ways to use it
- File/process attributes in Unix
- ACLs, capabilities, mandatory access control
- How do the MMU and the CPU privilege levels contribute to security?
- What is software-based protection, can you give an example?
- Which typical software bugs contribute to security problems, can you give examples?
Overview
- Overview of security problems
- Permission management
- System software and security
- Software bugs
- Examples
- Conclusions
Security problems
- Definitions of relevant terms
- Safety
- protection against risks due to hardware and software errors or failures
- Security
- protection of users and computers against intended errors (attacks)
- Safety
- Both topics are highly relevant for system software
- Today, we will only discuss security
- Exploitation of security holes
- malware
- social engineering
Operating system security
- Someone...
- differentiation of persons and groups of persons
- has to be deterred from doing...
- using technical and organizational methods
- some...
- limited only by our imagination
- unexpected things!
-
- unauthorized reading of data (secrecy, confidentiality),
-
- unauthorized writing of data (integrity),
-
- working under a "false flag" (authenticity),
-
- unauthorized use of resources (availability),
- etc…
-
- Differentiation between
- internal
- and external attacks
Example: fake login screen
- Attacker starts a user program that simulates a login screen
- The unsuspecting user enters username and (secret) password
- Attacker program records user name and password
- Attacker program terminates the current shell
- Login session of the attacker is closed and the regular login screen appears
- User assumes incorrectly typed password
- Remedy: require the user to start the login sequence using a key combination that cannot be intercepted by a user program
- e.g. CTRL-ALT-DEL in Windows NT and following
Malware example: viruses
- Program code inserted into another program, which can be replicated this way
- Virus sleeps until the infected program is executed
- Start of the infected program results in virus reproduction
- Execution of the virus functionality can be time-controlled
- Sorts of viruses
- Boot sector virus: executed at system startup time
- Macro virus: in scriptable programs, e.g. Word, Excel
- Reproduced through documents (e.g. sent by email)!
- Executable program as virus
- Distribution through…
- exchange of storage media (USB memory sticks etc.)
- email attachments
- web pages
Example: social engineering
- Not a system software problem
- …but very important
- Gain access to information by exploiting human errors
- Phishing
- obtain data of an internet user using forged addresses (e.g. with similar names/typos)
- e.g. by using forged emails from banks or government institutions
- Pharming
- manipulation of DNS requests by web browsers
- redirect accesses, e.g. to forged bank websites
- most users ignore browser warnings about invalid security certificates
- Phishing
Types of malware
- Viruses
- programs inadvertently distributed by a user
- infect other programs
- …and reproduce this way
- Worms
- do not wait for user actions to propagate to another computer
- actively try to invade new systems
- exploit security holes on target systems
- Trojan horses ("trojans")
- program disguised as useful application (or game…)
- in addition to the useful function, additional functionality is provided without the user noticing, e.g. providing an attacker with access to the local computer via internet
- Root kit
- collection of software tools to...
- disguise future logins of an attacker
- hide processes and files
- is installed after a computer system is compromised
- can hide itself and its activities from the user
- e.g. by manipulating tools to display processes (ps), directory contents (ls), network connections (netstat) ...
- …or by manipulating system-wide shared libraries (libc)
- …or directly by manipulating the OS kernel
- collection of software tools to...
- Often, malware uses a combination of these types
Permission management: objectives
- Protect stored information from
- breach of confidentiality
- theft of information
- unwanted manipulation (including encryption: ransomware)
- in all multi-user systems
- …and every system connected to the Internet is in fact a multi-user system!
Permission management: requirements
- All objects of a system must be uniquely and unforgeably identifiable
- (external) users of a system must be uniquely and unforgeably identifiable ➛ authentication
- Access to objects allowed only if the user has the required permissions
- Access to objects should only be allowed using the appropriate object management
- permissions must be stored in an unforgeable way; transfer of permissions must only take place it a controlled way
- it must be possible to validate basic protection mechanisms with low overhead
Permission management: design principles
- Principle of least privilege
- Allow a person or software component only those permissions that are required for the functionality to be realized
- Standard case: deny permission
- Counterexample: Unix "root"
- Fail-safe defaults
- Example: newly installed server software
- Separation of duties
- Multiple conditions exist to allow an operation
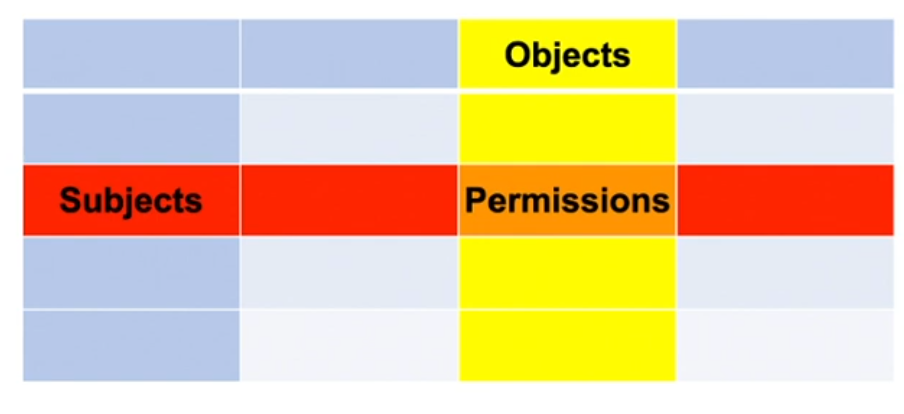
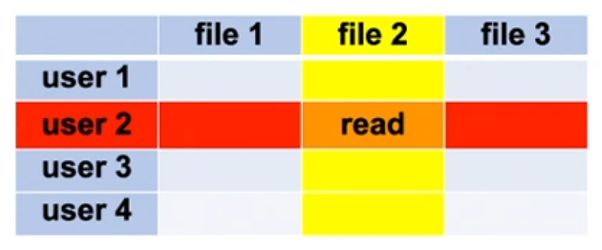
Access matrix
- Elements of the matrix:
- Subjects (persons/users, processes)
- Objects (data, devices, processes, memory, …)
- Operations (read, write, delete, execute, …)
- Question: Is
operation(subject, object)permitted? Objects Subjects Permissions
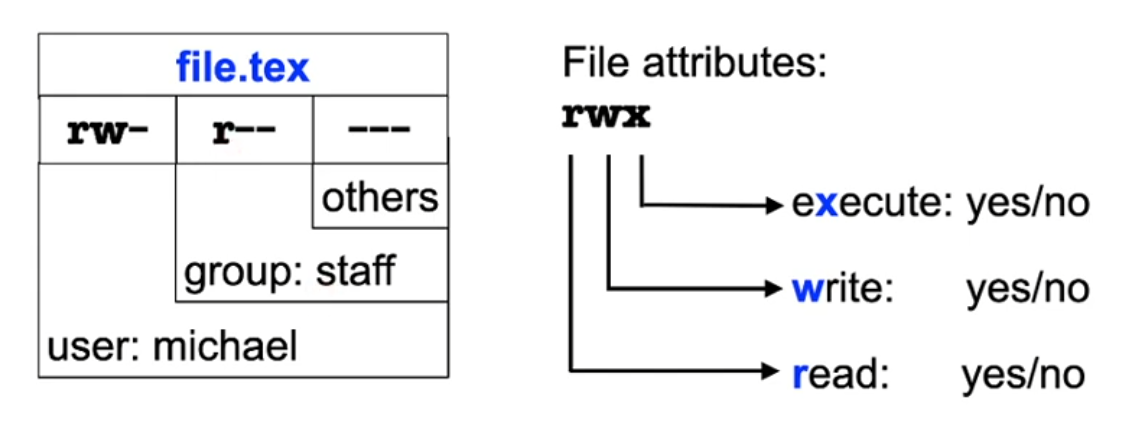
Basic model: file/process attributes
- Properties related to a user:
- for which user is the process being executed?
- which user is the owner of a file?
- which permissions does the owner of a file give to him/ herself and which permissions to other users?
- Permissions of a process when accessing a file
- Attributes of processes: user ID
- Attributes of files: owner ID
Access matrix variants
- Colums: ACL – Access Control Lists
- for every access to an object, the access permissions are validated based on the identity of the requesting subject (user)
- Rows: Capabilities
- for every access to an object a property is validated which is owned by the subject and which can be passed to other subjects on demand
- Rule-based: mandatory access control
- rules are evaluated for every access
ACLs
- Column-wise view of the access matrix: Access Control List (ACL)
- ACLs indicate for every object which subjects are allowed to perform which operations on it
- ACLs can be configured by…
- subjects having an appropriate ACL entry granting this permission
- the creator of the object (file)
- Example: Multics OS – triplet (user, group, permissions)
File 0 (Jan, *, RWX)
File 1 (Jan, system, RWX)
File 2 (Jan, *, RW-), (Els, staff, R--), (Maike, _, RW-)
File 3 (_, student, R--)
File 4 (Jelle, _,---), (_, student, R--)
- Windows (starting with NT)
- object: allow, deny
- full control, modify, read&execute,
Unix access permissions
- Unix: simple access control lists
- Processes have a user ID and a group ID
- Files have an owner and a group
- Permissions are related to the user (owner), group, and all others
Problem: permission extensions
- Example – keep a high score list for a game
- High score list: /home/me/games/tetris/highscores
- Program: /home/me/bin/games/tetris
- Every player should be able to enter his/her own high score
- all users have write permission to the high score list
- too many permissions (does not work)
- every user could arbitrarily manipulate the high score list
- SetUID: only "me" has write permissions
- Tetris program has "setuid" permissions
- as soon as the Tetris program is executed, the process is assigned the user ID of the owner of the executable program
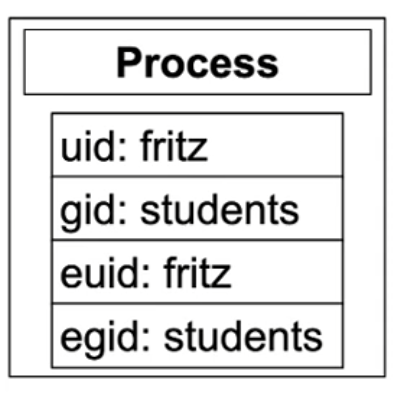
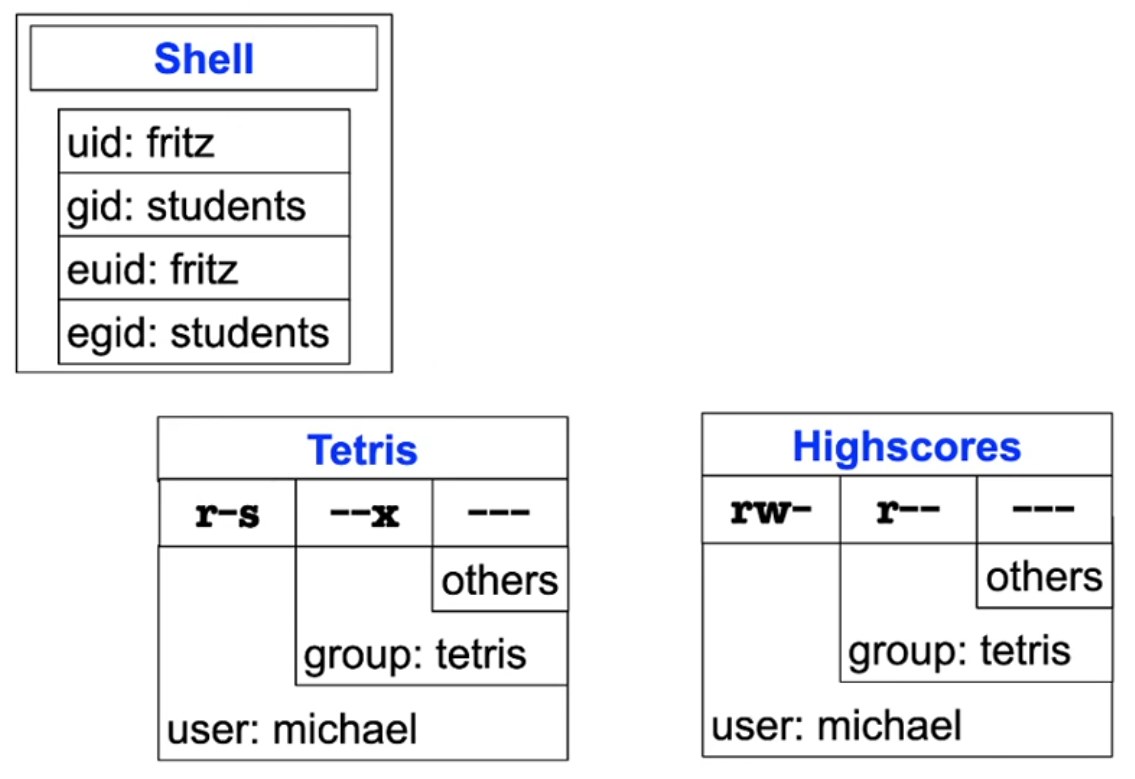
Unix: users and processes
- Each process represents a user
- Process attributes:
- User ID (uid), group ID (gid)
- Effective uid (euid), effective gid (egid)
- Determine permissions of a process when accessing files
- Only a few highly privileged processes are allowed to change their uid and gid
- e.g. the login process
- After verifying the user’s password, the login process sets uid, gid, euid and egid
- All other processes: children of login
- Child processes inherit the parent attributes
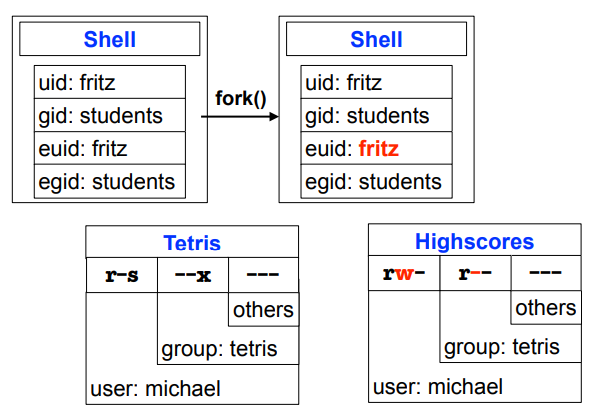
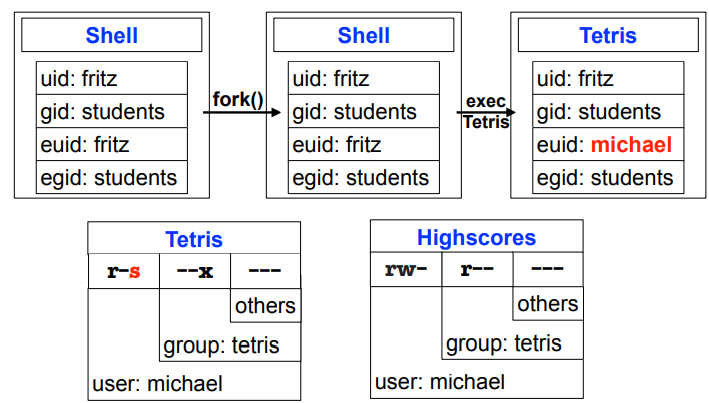
Unix solution: setuid mechanism
- File which contains trustworthy program code (e.g. Tetris) is given an additional permission bit: setuid (s bit)
- shown as "s" instead of "x" for executable in directory listing
- there is also a setgid bit (rarely used)
- exec of setuid programs:
- executing process obtains the UID of the program owner as effective UID
- precisely: the UID of the file containing the program
- Process execution performed using the permissions of this user as long as the program is not terminated
- Contradicts the principle of least privilege
- Workaround: create special user for the application instead of using "root"
- It is considered good programming style to return any setuid permissions as soon as they are no longer required by a process
- Contradicts the principle of least privilege
Example: high score list
Example: high score list (2)
Example: high score list (3)
setuid problems
- Extension of the permissions of a user exactly for the case of using the given program
- "Owner" of the program trusts the user who is using the program
- Owner can be the administrator, but also normal users
- "Owner" of the program trusts the user who is using the program
- Problem: program bugs
- can result in significant permission extensions
- e.g. enable calling a shell (with inherited permissions of the owner of the setuid process) from such a program
- Practical experience: still to many permissions granted!
Capabilities
- Row-wise view of the access matrix: Capability
- Capabilities indicate for each subject in which ways it is allowed to access which objects

Example
- Basic implementation: Unix file descriptors
- Propagated using the fork system call
- Allows access to files without repeated validation of the Unix access permissions

Rule-based access matrix
- Mandatory Access Control
- Concept:
- subjects and objects possess attributes ("labels")
- decision about granting access by evaluating rules
- Implemented in "security kernels", e.g. SELinux

System software and security
- Hardware-based protection
- MMU
- protection rings
- …complemented by protection in the system software
- Exclusive control of the hardware by the OS
- Exclusive control of all processes
- Exclusive control of all resources
- Provisioning of
- identification mechanisms
- authentication mechanisms
- privilege separation
- cryptographic protection of information
Hardware-based protection: MMU
- Memory Management Unit
- Hardware component of the CPU that translates and controls program accesses to memory
- Translation of the process view (virtual addresses) into the hardware view (physical addresses)
- Main memory is partitioned into pages
- Protection by...
- only mapping the exact set of required main memory pages into the virtual address space of a process
- isolation of the physical address spaces of different processes
- protection bits for each page, controlled at every access
- read/write/execute code
- access permitted in user mode/supervisor mode
Protection rings
- Privilege concept
- All code is executed in the context of a given protection ring
- Code running in ring 0 has access to all system resources
- User programs run in ring 3
- Rings 1 & 2 for OS-like code
- e.g. device drivers
- Rings restrict…
- the usable subset of processor machine instructions
- e.g. disabling interrupts (sei/cli) not permitted in rings > 0
- the accessible address range for the process
- disabling of I/O accesses
- the usable subset of processor machine instructions
Software-based protection
- Identification mechanisms
- Unix: user and group identification
- Numeric value
- Translated into texts (user and group names) durch lookup in /etc/passwd
- Resources are assigned an owner
- Superuser: uid = 0
- Has all permissions possible in the system
Software-based protection (2)
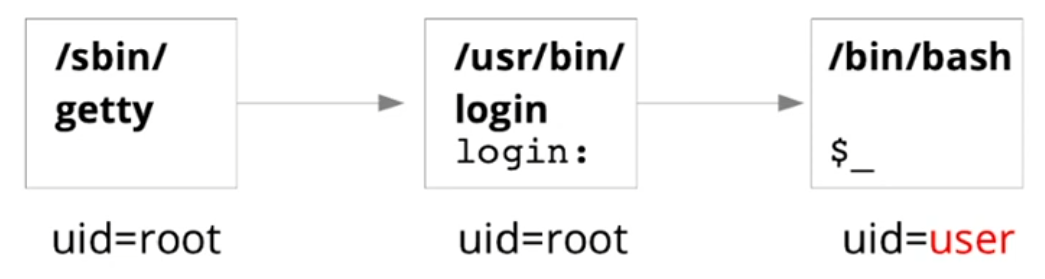
- Authentication mechanisms
- Unix login
- Reads user name and password
- Verification of the entered password with the one recorded in the system
- Either by encrypting the entered password and comparison with the recorded encrypted value
- Or by verification of a hash value
- The login process then starts the first user process (e.g., a shell) with the uid and gid of this user
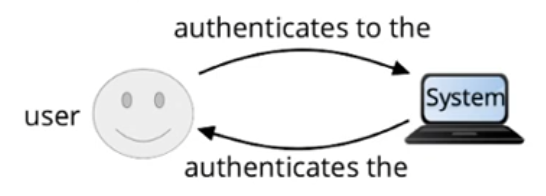
Software-based protection (3)
- Cryptographic protection of information
- e.g. DES encryption of user passwords
- Originally in Unix stored in the file /etc/passwd
root:4t6f4rt3423:0:0:System Administrator:/var/root:/bin/sh
daemon:ge53r3rfrg:1:1:System Services:/var/root:/usr/bin/false
me:1x3Fe5$gRd:1000:1000:Michael Engel:/home/me:/bin/bash
- Problem: encrypted passwords were readable for all users!
- …could be decrypted using a "brute force" attack given enough time
- readily available tools, e.g. "John the Ripper"
- Today: only user information stored in /etc/passwd
- Passwords are now stored separately in /etc/shadow!
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1353 May 28 22:43 /etc/passwd
-rw-r----- 1 root shadow 901 May 28 22:43 /etc/shadow
Software bugs
- Trade-off: performance ↔ security
- C, C++, Assembler: unmanaged languages
- Pointers, array bounds, value overflows
- C#, Java: managed languages
- Not usable for system software development!
- …why?
- Managed languages also have security problems!
- Problems
- Buffer overflows
- Value range overflows
- Error statistics
- One error per 1000 lines of code on average
- Independent of the implementation language!
Value ranges
- Problem: integer numbers are represented as bit strings with a limited number of bits
- Example: "char" data type in C
- Represented as signed 8 bit value
- Value range:-27 ... +27 – 1
- …or-128 ... +127
- The C code results in the following calculation in binary:
- Only the least significant 8 bits are significant
- thus the result =-126! char a = 127; char b = 3; char result = a + b;
char a = 127;
char b = 3;
char result = a + b;
01111111 (a)
+00000011 (b)
10000010 (result is negative!)
Value ranges (2)
- The following code results in problems:
char string[127] = "Hello World!\n"
char a = 127;
char b = 3;
...
char myfunc(char *string, char index) {
return string[index];
}
...
printf("%x", myfunc(string, a+b));
Heap overflow
- Heap: memory area for dynamically allocated data (e.g. via malloc)
- Buffer overflows in the heap can be problematic
- Memory ranges separately allocated with malloc can be contiguous in main memory
- There are no checks for overflows
- By passing incorrect sizes for data regions, an attacker can overwrite other data on the heap
- Example: Microsoft JPEG GDI+ (MS04-028)
- Size values in JPEG image files were not controlled
- "Normal" images files contain valid values
- These do not result in erroneous behavior
- Manipulated image files contain invalid values
- Overwrite other data on the heap
Heap overflow (2)
define BUFSIZE 16
define OVERSIZE 8 /* overflow buf2 by OVERSIZE bytes */
int main(void) {
u_long diff;
char *buf1 = malloc(BUFSIZE),
*buf2 = malloc(BUFSIZE);
diff = (u_long)buf2- (u_long)buf1;
printf("buf1 = %p, buf2 = %p, diff = 0x%x\n", buf1, buf2, diff);
memset(buf2, 'A', BUFSIZE-1);
buf2[BUFSIZE-1] = '\0';
printf("before overflow: buf2 = %s\n", buf2);
memset(buf1, 'B', (u_int)(diff + OVERSIZE));
printf("after overflow: buf2 = %s\n", buf2);
return 0;
}
Result…
- The value range is exceeded by 8 bytes

- buf1 exceeds its limit and arrives at the heap area in which buf2 is stored
- This heap area of buf2 still has valid contents
- Thus, the program does not terminate, but rather unexpectedly manipulates the data stored in buf2!
Unix Morris worm (sendmail)
- One of the first worms distributed over the Internet
- Written by a student of Cornell University, Robert Tappan Morris, and activated on November 2, 1988, from a computer at the MIT
- From the MIT to disguise the real origin of the worm
- Today, Robert Tappan Morris is professor at the MIT! :-)
- Exploited a security hole in the sendmail system
- Buffer overflow in gets()
- Written to determine the size of the Internet, should infect each system only once
- …but had a fatal bug in its replication function!
- 6000 Unix systems infected
- Cost of fixing damages estimated between US$10 and US$100 million
- …Morris was convicted to 3 years jail on probation and a US$10.000 fine...
Michelangelo virus
- First discovered in New Zealand in 1991
- Boot sector virus, infects e.g. MS-DOS systems
- Only uses BIOS functions, no DOS system calls
- Time-activated virus, active on March 6th
- Overwrites the first 100 sectors of the (first) hard disk with zeros
- Distribution using boot sectors of floppy disks
- Installed itself in the boot sector of the hard disk
- One of the first viruses broadly discussed in the media
- …but its effects were spectacularly exaggerated ;-)
- Some commercial software was accidentally delivered on disks with a boot sector virus
- Today: viruses on USB memory sticks, mobile phones with USB interfaces, …fresh from the factory!
Sony BMG root kit
- Software on copy protected CD-ROMs with Digital "Rights" Management (DRM) technology
- Filtering driver for CD-ROM drives and IDE disk controllers to control access to media
- Installed without informing the user or asking for approval
- Control over the use of data of Sony BMG
- …on Windows systems
- Hidden from analysis using root kit functionality
- Does not appear in the installed software list of the Windows control center and is not removable using uninstaller tools
- Does not only hide related files, directories, processes and registry entries, but globally everything starting with the string
- Enables other malware to hide itself using this root kit functionality!
Blue Pill – VM-based root kit
- Discovery and removal of root kits on OS level is possible
- But costly
- Objective: "undiscoverable" root kit
- "Blue Pill" tried to infect a PC with a root kit without requiring a system reboot
- Exploits hardware virtualization technology of current CPUs
- No (significant) performance impact
- All devices, e.g. GPUs, continue to be fully available to the OS
- Undiscoverable, since the OS does not notice that it is now running in a virtual machine
- …but there are still side effects that enable the detection of root kits like this
Conclusion
- Security gains increasing relevance in networked environments
- Extremely significant damages due to viruses, phishing, bot nets, ransomware, ...
- Experienced computer users are not safe either!
- Security checks in code are essential!
- Automated tests cannot find all errors; manual audits still required
- Still, security problems are unavoidable
- Thus, system software has to be constantly updated
- Whack-a-mole game…
- "Zero day exploits", newly discovered security holes which are not yet published (or fixed) are extremely dangerous
- Reaction time of system software vendors are in the range of hours to months…
- Hardware is also increasingly problematic: "Meltdown" and "Spectre"